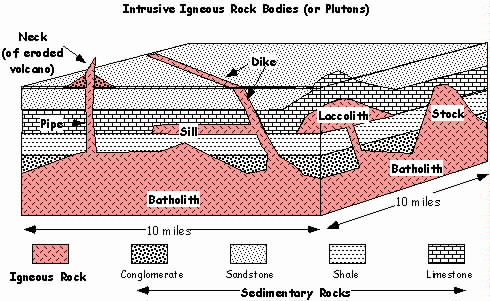
There are several types of cross-cutting relationships. Recall that intrusive igneous rocks rise from deep in the Earth towards the surface due to density differences (much like hot air balloons rise). The rise of magma may fracture the overlying rock, allowing the molten magma to fill the fractures and cool into a solid rock beneath the surface. Note that the igneous rocks must be younger than the other rocks (the conglomerate sandstone, shale, and limestone). That is, the layerd rocks had to already be there in order to be intruded. The Principle of Crosscutting Relationships states that a crosscutting rock is younger than the rocks it cuts. It's like saying you have to have a cake before you can cut it.
